层与层之间的通信
除了为架构的每个组件定义清晰的职责外,还需要考虑组件如何通信。这既包括规定通信规则,也包括组件如何通信的技术实现。应用程序的架构应该回答以下问题:
- 哪些组件可以与其他哪些组件通信(包括同类型的组件)?
- 这些组件之间互相暴露哪些输出?
- 任何给定的层是如何“连接”到另一层的?
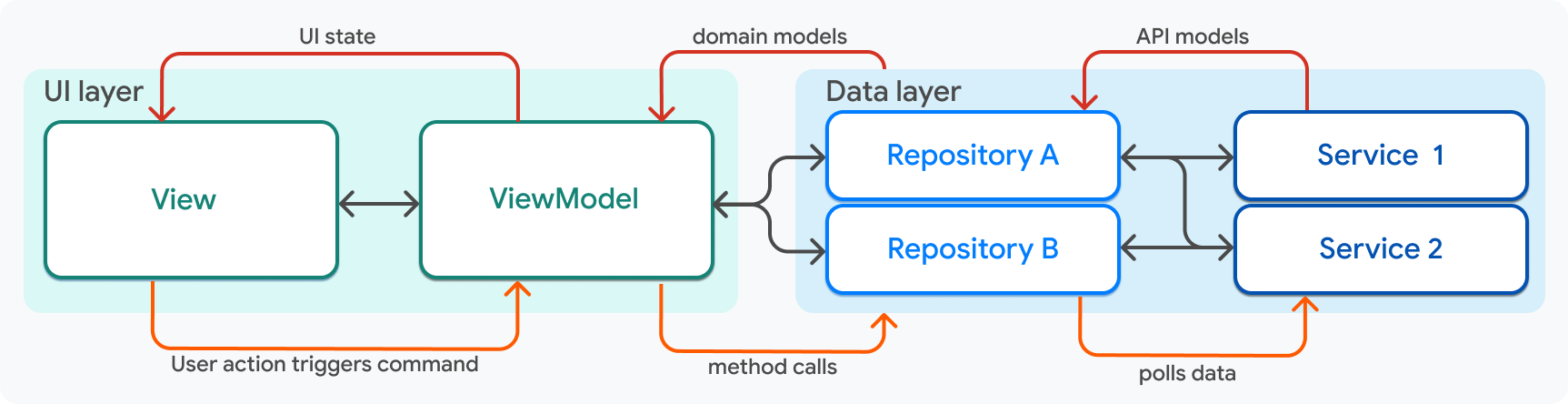
使用此图作为指南,交互规则如下:
| 组件 | 交互规则 |
|---|---|
| 视图 (View) |
|
| 视图模型 (ViewModel) |
|
| 存储库 (Repository) |
|
| 服务 (Service) |
|
依赖注入
#本指南展示了这些不同的组件如何通过使用输入和输出来相互通信。在所有情况下,两个层之间的通信都通过将一个组件传递到(消耗其数据的)组件的构造函数方法中来促进,例如将 Service 传递到 Repository 中。
class MyRepository {
MyRepository({required MyService myService})
: _myService = myService;
late final MyService _myService;
}然而,还有一件事缺失了,那就是对象的创建。在应用程序的哪个地方创建 MyService 实例,以便将其传递给 MyRepository?这个问题的答案涉及到一个称为依赖注入的模式。
在 Compass 应用中,依赖注入 是使用 package:provider 处理的。根据他们构建 Flutter 应用的经验,Google 的团队建议使用 package:provider 来实现依赖注入。
服务和存储库作为 Provider 对象暴露给 Flutter 应用程序的顶层 Widget 树。
runApp(
MultiProvider(
providers: [
Provider(create: (context) => AuthApiClient()),
Provider(create: (context) => ApiClient()),
Provider(create: (context) => SharedPreferencesService()),
ChangeNotifierProvider(
create: (context) => AuthRepositoryRemote(
authApiClient: context.read(),
apiClient: context.read(),
sharedPreferencesService: context.read(),
) as AuthRepository,
),
Provider(create: (context) =>
DestinationRepositoryRemote(
apiClient: context.read(),
) as DestinationRepository,
),
Provider(create: (context) =>
ContinentRepositoryRemote(
apiClient: context.read(),
) as ContinentRepository,
),
// In the Compass app, additional service and repository providers live here.
],
child: const MainApp(),
),
);服务仅被暴露出来,以便可以通过 provider 中的 BuildContext.read 方法立即注入到存储库中,如前面的代码片段所示。然后,存储库会被暴露出来,以便根据需要注入到视图模型中。
在 Widget 树的稍低层级,对应于整个屏幕的视图模型是在 package:go_router 配置中创建的,其中再次使用 provider 来注入必要的存储库。
// This code was modified for demo purposes.
GoRouter router(
AuthRepository authRepository,
) =>
GoRouter(
initialLocation: Routes.home,
debugLogDiagnostics: true,
redirect: _redirect,
refreshListenable: authRepository,
routes: [
GoRoute(
path: Routes.login,
builder: (context, state) {
return LoginScreen(
viewModel: LoginViewModel(
authRepository: context.read(),
),
);
},
),
GoRoute(
path: Routes.home,
builder: (context, state) {
final viewModel = HomeViewModel(
bookingRepository: context.read(),
);
return HomeScreen(viewModel: viewModel);
},
routes: [
// ...
],
),
],
);在视图模型或存储库内部,注入的组件应该是私有的。例如,HomeViewModel 类如下所示:
class HomeViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
HomeViewModel({
required BookingRepository bookingRepository,
required UserRepository userRepository,
}) : _bookingRepository = bookingRepository,
_userRepository = userRepository;
final BookingRepository _bookingRepository;
final UserRepository _userRepository;
// ...
}私有方法可防止具有视图模型访问权限的视图直接调用存储库上的方法。
至此,Compass 应用的代码演练结束。本页仅介绍了与架构相关的代码,但并未讲述全部故事。大部分实用工具代码、Widget 代码和 UI 样式都被忽略了。请浏览 Compass 应用仓库中的代码,以获取遵循这些原则构建的健壮 Flutter 应用程序的完整示例。
反馈
#随着本网站该部分的不断发展,我们欢迎您的反馈!