使用 Firestore 添加多人游戏支持
多人游戏需要一种方法来同步玩家之间的游戏状态。广义上讲,存在两种类型的多人游戏:
高刷新率。这些游戏需要每秒同步多次游戏状态,且延迟低。这包括动作游戏、体育游戏、格斗游戏。
低刷新率。这些游戏只需要偶尔同步游戏状态,延迟影响较小。这包括纸牌游戏、策略游戏、益智游戏。
这类似于实时游戏与回合制游戏之间的区别,尽管这个类比并不完全恰当。例如,实时策略游戏——顾名思义——是实时运行的,但这并不意味着高刷新率。这些游戏可以在玩家交互之间在本地机器上模拟大部分发生的事情。因此,它们不需要经常同步游戏状态。
如果你作为开发者可以选择低刷新率,你应该这样做。低刷新率可以降低延迟要求和服务器成本。有时,游戏需要高刷新率的同步。对于这些情况,Firestore 等解决方案**不太适合**。选择专用的多人服务器解决方案,例如 Nakama。Nakama 有一个 Dart 包。
如果你预计你的游戏需要低刷新率的同步,请继续阅读。
本教程演示如何使用 cloud_firestore 包 在你的游戏中实现多人游戏功能。本教程不需要服务器。它使用两个或更多客户端通过 Cloud Firestore 共享游戏状态。
1. 为多人游戏准备你的游戏
#编写你的游戏代码,使其能够响应本地事件和远程事件来更改游戏状态。本地事件可以是玩家动作或某些游戏逻辑。远程事件可以是来自服务器的世界更新。
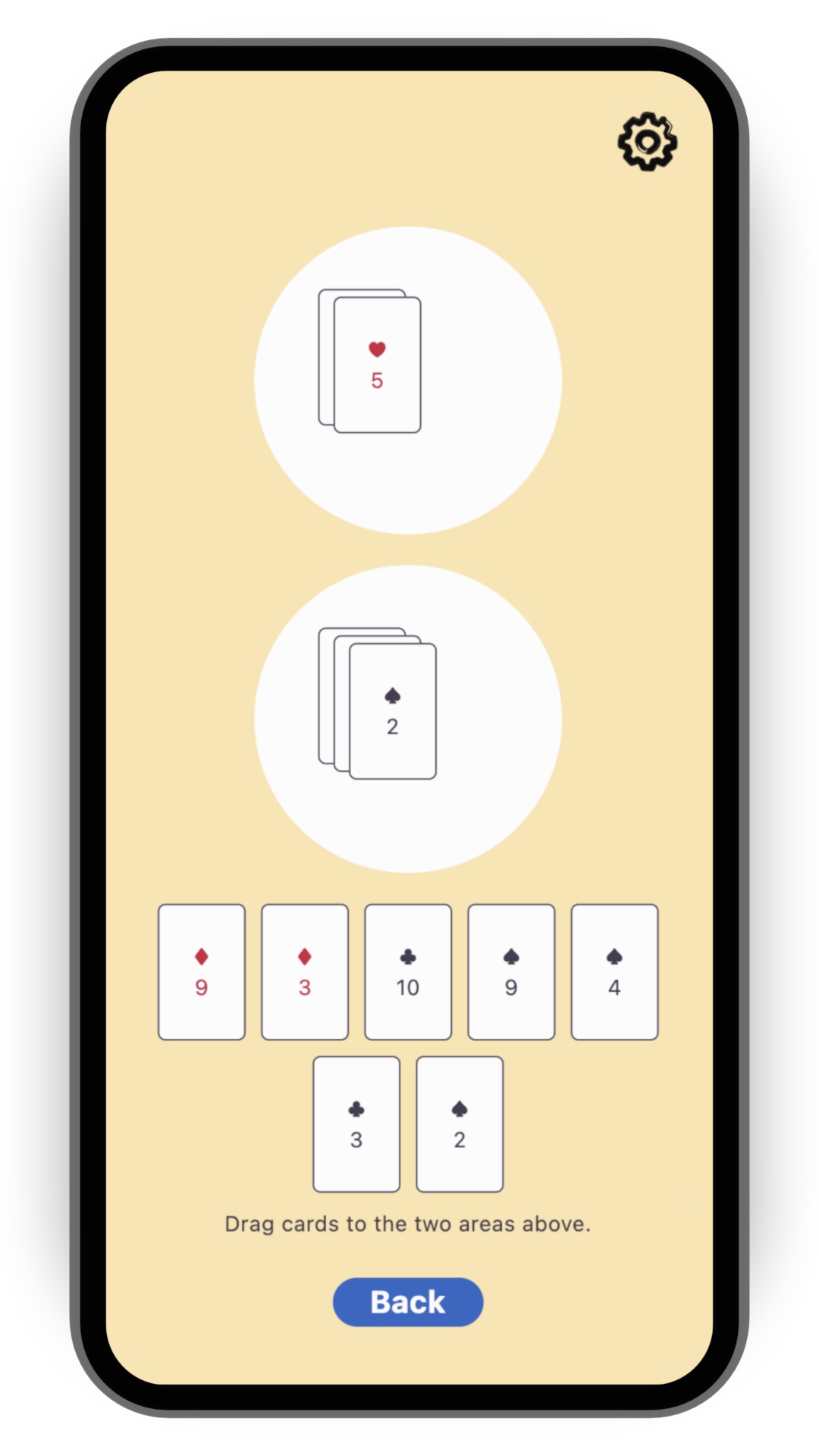
为了简化本食谱,请从 flutter/games 仓库 中的 card 模板开始。运行以下命令克隆该仓库:
git clone https://github.com/flutter/games.git打开 templates/card 中的项目。
2. 安装 Firestore
#Cloud Firestore 是一个可水平扩展的云端 NoSQL 文档数据库。它包含内置的实时同步功能。这非常适合我们的需求。它使游戏状态在云数据库中保持更新,因此每个玩家都能看到相同的状态。
如果你想快速了解 Cloud Firestore 的 15 分钟入门知识,请查看以下视频:
要将 Firestore 添加到你的 Flutter 项目中,请按照 Cloud Firestore 入门 指南的前两个步骤操作:
预期结果包括:
- 一个已在云端准备就绪的 Firestore 数据库,处于**测试模式**
- 一个生成的
firebase_options.dart文件 - 已将适当的插件添加到你的
pubspec.yaml
你**无需**在此步骤中编写任何 Dart 代码。一旦你理解了该指南中编写 Dart 代码的步骤,请返回本教程。
3. 初始化 Firestore
#打开
lib/main.dart并导入插件,以及上一步中由flutterfire configure生成的firebase_options.dart文件。dartimport 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart'; import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart'; import 'firebase_options.dart';在
lib/main.dart中,在调用runApp()的正上方添加以下代码:dartWidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized(); await Firebase.initializeApp(options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform);这确保了 Firebase 在游戏启动时被初始化。
将 Firestore 实例添加到应用程序。这样,任何小部件都可以访问此实例。如果需要,小部件也可以对实例的缺失做出反应。
要使用
card模板执行此操作,你可以使用provider包(它已作为依赖项安装)。将样板代码
runApp(MyApp())替换为以下内容:dartrunApp(Provider.value(value: FirebaseFirestore.instance, child: MyApp()));将 provider 放在
MyApp外部,而不是内部。这使你可以在没有 Firebase 的情况下测试应用程序。
4. 创建一个 Firestore 控制器类
#虽然你可以直接与 Firestore 通信,但你应该编写一个专用的控制器类,使代码更具可读性和可维护性。
控制器的实现方式取决于你的游戏和多人游戏体验的具体设计。对于 card 模板的情况,你可以同步两个圆形游戏区域的内容。这不足以提供完整的多人游戏体验,但这是一个很好的开始。
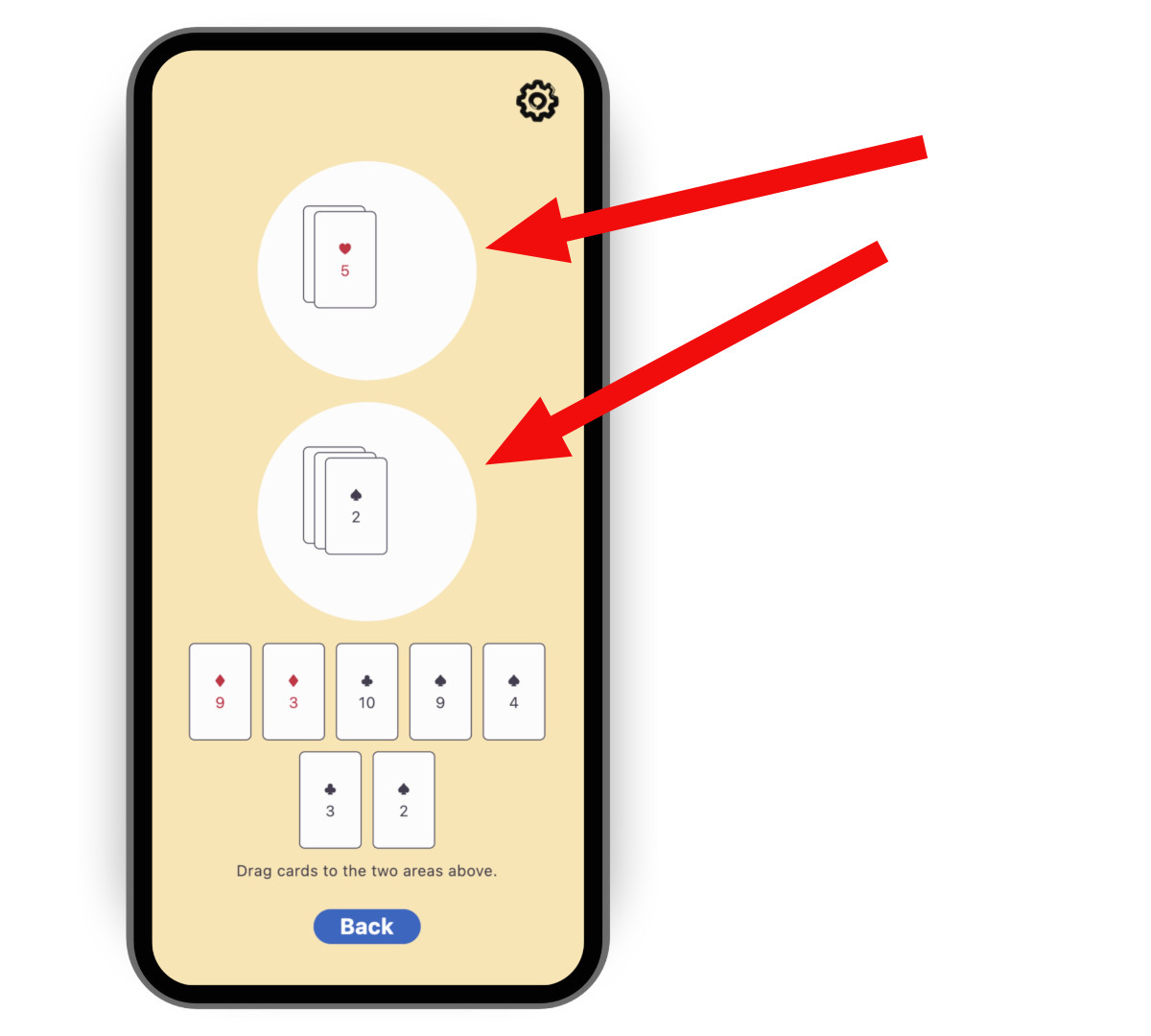
要创建控制器,请复制以下代码,然后将其粘贴到一个名为 lib/multiplayer/firestore_controller.dart 的新文件中。
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart';
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'package:logging/logging.dart';
import '../game_internals/board_state.dart';
import '../game_internals/playing_area.dart';
import '../game_internals/playing_card.dart';
class FirestoreController {
static final _log = Logger('FirestoreController');
final FirebaseFirestore instance;
final BoardState boardState;
/// For now, there is only one match. But in order to be ready
/// for match-making, put it in a Firestore collection called matches.
late final _matchRef = instance.collection('matches').doc('match_1');
late final _areaOneRef = _matchRef
.collection('areas')
.doc('area_one')
.withConverter<List<PlayingCard>>(
fromFirestore: _cardsFromFirestore,
toFirestore: _cardsToFirestore,
);
late final _areaTwoRef = _matchRef
.collection('areas')
.doc('area_two')
.withConverter<List<PlayingCard>>(
fromFirestore: _cardsFromFirestore,
toFirestore: _cardsToFirestore,
);
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaOneFirestoreSubscription;
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaTwoFirestoreSubscription;
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaOneLocalSubscription;
late final StreamSubscription<void> _areaTwoLocalSubscription;
FirestoreController({required this.instance, required this.boardState}) {
// Subscribe to the remote changes (from Firestore).
_areaOneFirestoreSubscription = _areaOneRef.snapshots().listen((snapshot) {
_updateLocalFromFirestore(boardState.areaOne, snapshot);
});
_areaTwoFirestoreSubscription = _areaTwoRef.snapshots().listen((snapshot) {
_updateLocalFromFirestore(boardState.areaTwo, snapshot);
});
// Subscribe to the local changes in game state.
_areaOneLocalSubscription = boardState.areaOne.playerChanges.listen((_) {
_updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaOne();
});
_areaTwoLocalSubscription = boardState.areaTwo.playerChanges.listen((_) {
_updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaTwo();
});
_log.fine('Initialized');
}
void dispose() {
_areaOneFirestoreSubscription.cancel();
_areaTwoFirestoreSubscription.cancel();
_areaOneLocalSubscription.cancel();
_areaTwoLocalSubscription.cancel();
_log.fine('Disposed');
}
/// Takes the raw JSON snapshot coming from Firestore and attempts to
/// convert it into a list of [PlayingCard]s.
List<PlayingCard> _cardsFromFirestore(
DocumentSnapshot<Map<String, Object?>> snapshot,
SnapshotOptions? options,
) {
final data = snapshot.data()?['cards'] as List<Object?>?;
if (data == null) {
_log.info('No data found on Firestore, returning empty list');
return [];
}
try {
return data
.cast<Map<String, Object?>>()
.map(PlayingCard.fromJson)
.toList();
} catch (e) {
throw FirebaseControllerException(
'Failed to parse data from Firestore: $e',
);
}
}
/// Takes a list of [PlayingCard]s and converts it into a JSON object
/// that can be saved into Firestore.
Map<String, Object?> _cardsToFirestore(
List<PlayingCard> cards,
SetOptions? options,
) {
return {'cards': cards.map((c) => c.toJson()).toList()};
}
/// Updates Firestore with the local state of [area].
Future<void> _updateFirestoreFromLocal(
PlayingArea area,
DocumentReference<List<PlayingCard>> ref,
) async {
try {
_log.fine('Updating Firestore with local data (${area.cards}) ...');
await ref.set(area.cards);
_log.fine('... done updating.');
} catch (e) {
throw FirebaseControllerException(
'Failed to update Firestore with local data (${area.cards}): $e',
);
}
}
/// Sends the local state of `boardState.areaOne` to Firestore.
void _updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaOne() {
_updateFirestoreFromLocal(boardState.areaOne, _areaOneRef);
}
/// Sends the local state of `boardState.areaTwo` to Firestore.
void _updateFirestoreFromLocalAreaTwo() {
_updateFirestoreFromLocal(boardState.areaTwo, _areaTwoRef);
}
/// Updates the local state of [area] with the data from Firestore.
void _updateLocalFromFirestore(
PlayingArea area,
DocumentSnapshot<List<PlayingCard>> snapshot,
) {
_log.fine('Received new data from Firestore (${snapshot.data()})');
final cards = snapshot.data() ?? [];
if (listEquals(cards, area.cards)) {
_log.fine('No change');
} else {
_log.fine('Updating local data with Firestore data ($cards)');
area.replaceWith(cards);
}
}
}
class FirebaseControllerException implements Exception {
final String message;
FirebaseControllerException(this.message);
@override
String toString() => 'FirebaseControllerException: $message';
}请注意此代码的以下特点:
控制器的构造函数接受一个
BoardState。这使得控制器能够操作游戏本地状态。控制器订阅本地更改以更新 Firestore,并订阅远程更改以更新本地状态和 UI。
字段
_areaOneRef和_areaTwoRef是 Firebase 文档引用。它们描述了每个区域的数据驻留位置,以及如何在本地 Dart 对象 (List) 和远程 JSON 对象 (Map) 之间进行转换。Firestore API 允许我们使用.snapshots()订阅这些引用,并使用.set()写入它们。
5. 使用 Firestore 控制器
#打开负责启动游戏会话的文件:对于
card模板,是lib/play_session/play_session_screen.dart。你将从该文件实例化 Firestore 控制器。导入 Firebase 和控制器
dartimport 'package:cloud_firestore/cloud_firestore.dart'; import '../multiplayer/firestore_controller.dart';在
_PlaySessionScreenState类中添加一个可空字段以包含控制器实例dartFirestoreController? _firestoreController;在同一个类的
initState()方法中,添加尝试读取 FirebaseFirestore 实例的代码,如果成功,则构造控制器。你已在“初始化 Firestore”步骤中将FirebaseFirestore实例添加到main.dart。dartfinal firestore = context.read<FirebaseFirestore?>(); if (firestore == null) { _log.warning( "Firestore instance wasn't provided. " 'Running without _firestoreController.', ); } else { _firestoreController = FirestoreController( instance: firestore, boardState: _boardState, ); }使用同一个类的
dispose()方法处理控制器。dart_firestoreController?.dispose();
6. 测试游戏
#在两个独立的设备上或在同一设备的两个不同窗口中运行游戏。
观察在一个设备上向某个区域添加卡片后,它如何出现在另一个设备上。
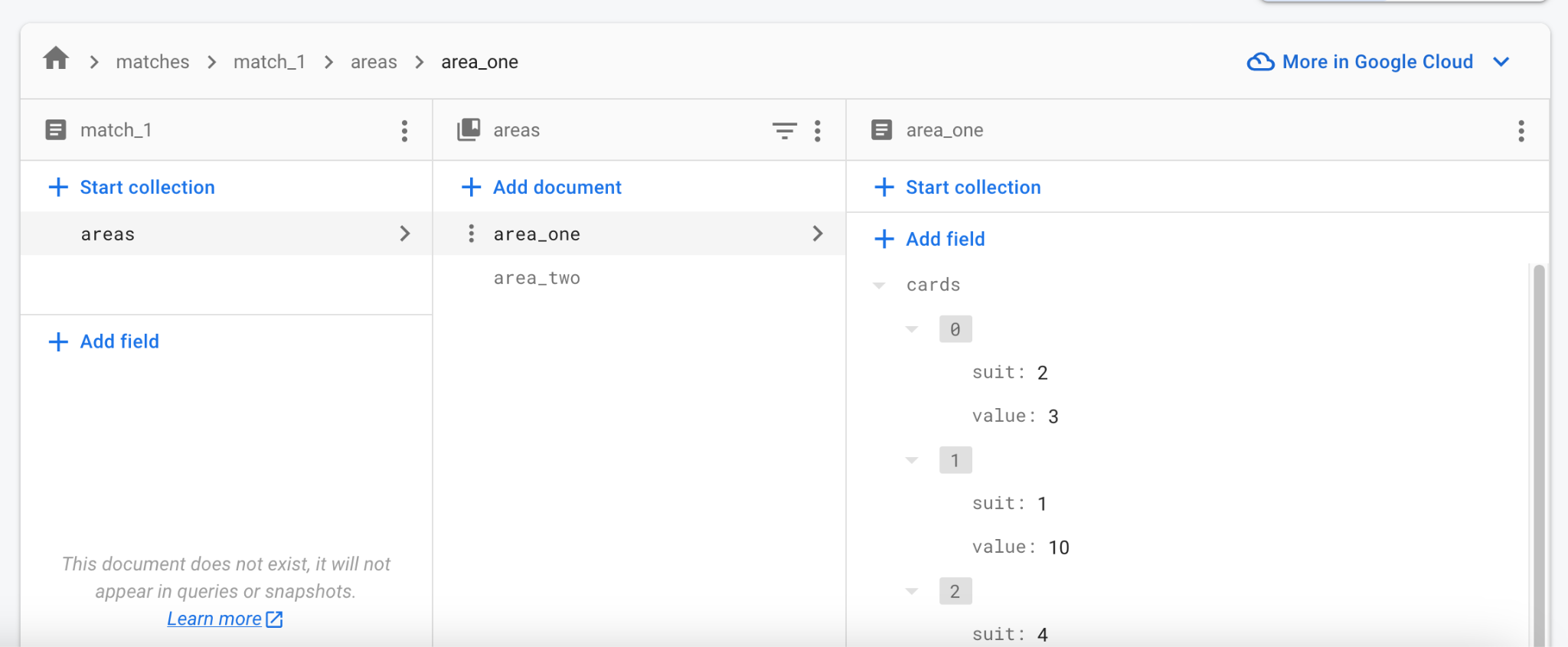
打开 Firebase Web 控制台并导航到你的项目的 Firestore 数据库。
观察它是如何实时更新数据的。你甚至可以在控制台中编辑数据,并看到所有正在运行的客户端都在更新。
故障排除
#测试 Firebase 集成时最常见的问题包括:
尝试访问 Firebase 时游戏崩溃。
- Firebase 集成未正确设置。请重新访问**步骤 2**,并确保在该步骤中运行了
flutterfire configure。
- Firebase 集成未正确设置。请重新访问**步骤 2**,并确保在该步骤中运行了
游戏无法在 macOS 上与 Firebase 通信。
- 默认情况下,macOS 应用程序没有互联网访问权限。首先启用互联网授权。
7. 后续步骤
#至此,游戏已实现客户端之间近乎即时且可靠的状态同步。它缺乏实际的游戏规则:何时可以打出哪些牌,以及结果如何。这取决于游戏本身,留给你尝试。

此时,比赛的共享状态只包括两个游戏区域及其中的牌。你也可以将其他数据保存到 _matchRef 中,例如玩家是谁以及轮到谁。如果你不确定从何开始,请按照一两个 Firestore codelab 来熟悉 API。
起初,单个匹配足以与同事和朋友测试你的多人游戏。随着发布日期的临近,请考虑身份验证和匹配。值得庆幸的是,Firebase 提供了一种内置的用户身份验证方式,并且 Firestore 数据库结构可以处理多个匹配。你可以用所需数量的记录填充匹配集合,而不是单个 match_1。
在线匹配可以从“等待”状态开始,只有第一个玩家在场。其他玩家可以在某种大厅中看到“等待”匹配。一旦有足够多的玩家加入匹配,它就会变为“活动”状态。同样,具体实现取决于你想要的在线体验。基本原理保持不变:一个大型文档集合,每个文档代表一个活动或潜在的匹配。